Digital Security: Understand the Role of WAF (Web Application Firewall) in Web Environments
Discover how WAF protects web applications against cyber attacks, improves performance and ensures compliance with security standards.

Diego Aron Gomes

Digital transformation has brought countless opportunities for companies, but has also opened the way for increasingly sophisticated threats. With cyber attacks evolving daily, traditional protections, such as network firewalls, are no longer sufficient to ensure application security.
In this context, the Web Application Firewall (WAF) emerges as an indispensable solution to protect sensitive data and maintain application stability.
What is a Web Application Firewall (WAF)?
The Web Application Firewall (WAF) is an additional layer of protection created to protect web applications by monitoring and filtering malicious traffic. Unlike traditional firewalls, which operate at network layers (OSI Layers 3 and 4), WAF operates directly at the application layer (Layer 7).
Main threats blocked by WAF:
SQL Injection attacks
XSS attacks
CSRF attacks
Endpoint exploitation
Application-targeted
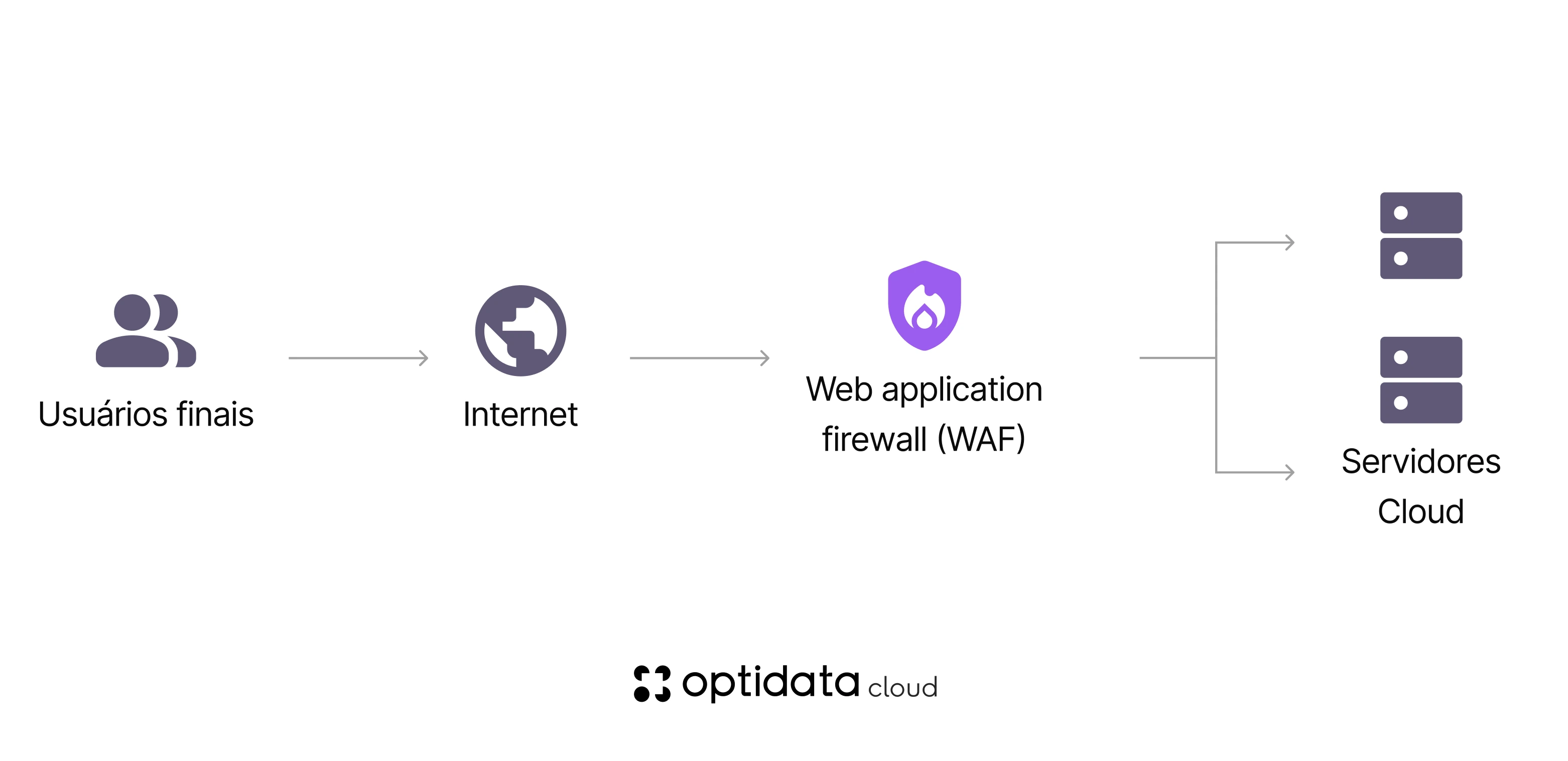
How WAF works in practice
By analyzing requests sent to the server, WAF functions as a "digital doorman". It blocks suspicious or malicious behavior patterns before they reach the backend, protecting both the application and users.
Advanced technology: Many WAF versions, such as Next-Gen WAFs, use machine learning and artificial intelligence to identify and block new threats as they emerge.
This protection is essential for companies that deal with:
- E-commerce and virtual stores
- SaaS platforms
- Digital banks and fintechs
- Environments that process sensitive data
Main Benefits of WAF in IT Environments
Implementing a Web Application Firewall brings several advantages not only in security, but also in operational performance.
1. Protection against Main Cyber Attacks
As an advanced solution, WAF protects companies against threats listed in the OWASP Top 10, the most common vulnerabilities in web applications.
- Injection Attacks (e.g.: SQL Injection): Exploitation of flaws to manipulate databases.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Attacks that inject malicious scripts to steal information or execute commands.
- Broken Authentication: Exploitation of flaws in authentication methods and session management.
- Vulnerable APIs: Protection against exposure of poorly designed or misconfigured endpoints.
Result: With active protection against these vulnerabilities, WAF drastically reduces risks of intrusion, data leakage or operational interruptions.
2. Compliance with Security Standards and Regulations
IT companies need to meet standards such as LGPD, GDPR and PCI DSS to maintain business integrity and comply with legal requirements.
WAF facilitates this process by:
- Making brute force attacks with leakage possibility difficult
- Monitoring suspicious access and violation attempts
- Maintaining encryption and access control policies
Additional benefit: Implementing a WAF adjusted to your sector's requirements not only reduces legal risks, but also strengthens the company's reputation as a trusted partner.
3. Scalability and Operational Cost Reduction
Beyond security, WAF optimizes infrastructure, blocking malicious traffic before it reaches servers.
Tip: A solution like CDN-based WAF, which combines protection with content delivery networks, also improves application response time for end users.
4. User Experience Improvement
A secure application is more reliable and stable, which directly improves user experience.
By preventing attacks and restricting illegitimate access:
- Loading time is optimized
- Applications remain available even in high traffic scenarios
- Problems like slowness or interruptions caused by DDoS attacks are avoided
Types of WAF Available in the Market
WAF can be implemented in various ways, offering flexibility according to operational contexts. Learn about the main types and their characteristics:
1. Network WAF
HOW IT WORKS
Deployed directly on hardware that controls local network traffic (on-premises).
High performance and low latency; ideal for applications that require fast responses.
High operational costs and greater complexity in maintenance.
2. Host WAF
HOW IT WORKS
Software-based, can be embedded directly into application code.
Advanced customization, ideal for companies that need specific rules.
Depends on server computational resources; may increase management complexity.
3. Cloud WAF
HOW IT WORKS
Offered as a managed service in SaaS (Software as a Service) model.
Easy to implement, scalable and accessible. No infrastructure investment required.
Some advanced configurations may be limited, depending on the provider.
4. CDN WAF
HOW IT WORKS
Combines WAF protection with content distribution through a CDN.
Reduces latency and improves global application performance.
Global companies or high-traffic platforms.
5. Next-Gen WAF
ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY
Uses artificial intelligence and machine learning to detect anomalous behaviors and emerging threats.
Maximum proactive protection against new and complex attacks.
How Optidata Can Help with Digital Protection
When looking for tailored security solutions, it's essential to have specialized partners. Optidata offers a comprehensive approach to protect your digital infrastructure.
💡 Strategic Consulting
We help your IT team choose and implement the ideal WAF for your infrastructure, ensuring maximum efficiency.
⚙️ Managed Services
We offer configuration, monitoring and continuous updating of Web Application Firewalls for your peace of mind.
🛡️ Robust Infrastructure
Our solutions are built on robust and scalable infrastructures to protect your applications against any threat.
Our Commitment: Whether with a Next-Gen WAF or cloud solutions, Optidata is committed to optimizing your organization's security without compromising performance.